Scope
This information refers to silver graphite
profiles and contact tips manufactured by
blending of silver and graphite powder,
compacting, sintering, extruding and rolling.
The deformation results in the alignment
of graphite particles along the direction
of the extrusion and rolling. A brazeable
silver side is produced by decarburization.
Profiles clad with a brazing alloy and
presoldered contact tips are available.
DESIGNATION OF
STANDARD COMPOSITIONS
Profiles show a parallel orientation of the
graphite to the contact surface and can be
produced with 2 and 3 weight percent
graphite. contact tips with 2,3,4 and 5% are
available either with the parallel orientation
(AgC II) or with a perpendicular orientation
of the graphite to the contact surface (AgC!)
Applications
- circuit breakers
- earth leakage breakers
- miniature circuit breakers
CHARACTERISTICS
- best anti-welding properties of all contact
materials on make with C-contents of 3%
and higher (better with graphite particle
alignment parallel to contact side)
- best protection against contact welding
of closed contacts under short ciruit
currents
- low erosion on make
- low contact resistance
- reduced erosion on break with
perpendicular graphite particle alignment to contact surface
- inferior are migration properties; compensated by
asymmetrical material combinations:
- Cu counter-contact with low currents
-
AgNi counter-contact with high currents
MICROSTRUCTURE
The directional deformation of the material during the
manufacturing process causes a strong displacement of
the graphite particles into graphite layers.
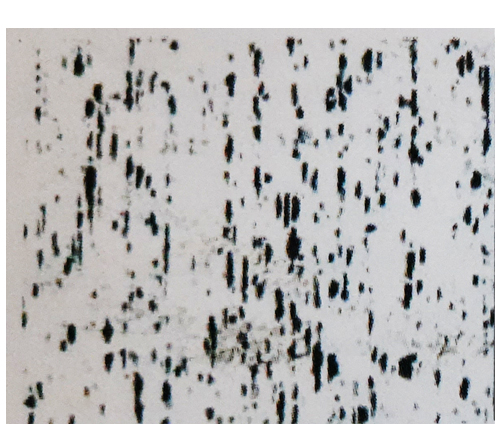
Longitudinal Sectional
(parallel to the diretion
of extrusion)
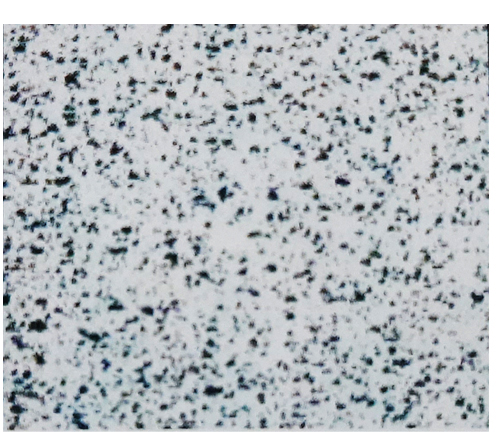
AgC
3
Cross Section
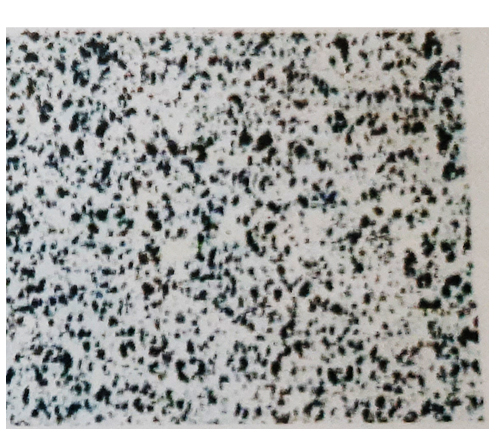
AgC
5
Cross Section
Physical Properties
| Material |
AgC2 |
AgC3 |
AgC4 |
AgC5 |
| Density [g/cm3] |
9.4 |
9.1 |
8.8 |
8.6 |
| Electrical Conductivity [m/(Ω.mm2)] |
47 |
47 |
44 |
43.5 |
| Hardness Soft [HV1] |
35 |
35 |
35 |
35 |
 Longitudinal Sectional
Longitudinal Sectional AgC3
AgC3 AgC5
AgC5